INTRODUCTION
India's textiles sector is one of the oldest industries in the Indian economy, dating back to several centuries.
The industry is extremely varied, with hand-spun and hand-woven textiles sectors at one end of the spectrum, with the capital-intensive sophisticated mills sector on the other end. The decentralised power looms/ hosiery and knitting sector forms the largest component in the textiles sector. The close linkage of textiles industry to agriculture (for raw materials such as cotton) and the ancient culture and traditions of the country in terms of textiles makes it unique in comparison to other industries in the country. India's textiles industry has a capacity to produce a wide variety of products suitable for different market segments, both within India and across the world.

MARKET SIZE
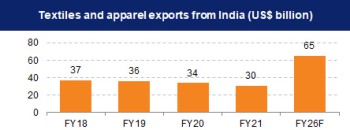
India's textiles industry has around 4.5 crore employed workers including 35.22 lakh handloom workers across the country. Exports of textiles (RMG of all textiles, cotton yarns/fabs/made-ups/handloom products, man-made yarns/fabs/made-ups, handicrafts excluding handmade carpets, carpets and jute mfg. including floor coverings) stood at US$ 29.8 billion between April-December 2021.
The Indian textiles market is expected to be worth more than US$ 209 billion by 2029.
India is the world's largest producer of cotton. Production stood at 360.13 lakh bales for the crop year October 2021-September 2022. Domestic consumption for the 2021-22 crop year is estimated to be at 335 lakh bales.
Production of fibre in India reached 2.40 MT in FY21 (till January 2021), while that for yarn, the production stood at 4,762 million kgs during same period.
India's home textile exports grew at a healthy rate of 9% in FY21 despite the pandemic. In the year 2020-21, 1.13 million tonnes of cotton yarn were exported from India.
INVESTMENT
The textiles sector has witnessed a spurt in investment during the last five years. The industry (including dyed and printed) attracted Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) worth US$ 3.93 billion from April 2000-December 2021.
In November 2021, Federico Salas, the Mexican Ambassador to India, visited the Khadi India Pavilion at the India International Trade Fair 2021 and suggested that India and Mexico should come together to promote Khadi globally.
Companies in home textile are using technology to optimise the value chain. For example, in October 2021, Welspun India introduced Wel-Trak 2.0—an upgraded, patented end-to-end traceability technology—to track textile raw materials throughout the supply chain.
Home textile companies in India are also leveraging strategic partnerships to strengthen their business operations and foothold in the country.
In October 2021, Welspun India collaborated with DuPont Biomaterials to introduce a home textile range and strengthen the company's sustainable textiles business.
In May 2021, Indo Count Industries Ltd. (ICIL), announced an investment of Rs. 200 crore (US$ 26.9 million) to expand its production capacity.
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES
Indian government has come up with several export promotion policies for the textiles sector. It has also allowed 100% FDI in the sector under the automatic route. The Rs. 10,683 crore (US$ 1.44 billion) PLI scheme is expected to be a major booster for the textile manufacturers. The scheme proposes to incentivise MMF (man-made fibre) apparel, MMF fabrics and 10 segments of technical textiles products.
Other Initiatives taken by Government of India are:
- In March 2022, the Bihar government submitted a proposal to the Union Textiles Ministry to set up a mega hub under the PM Mitra Mega Textile Park.
- In March 2022, Tamil Nadu Chief Minister Mr. MK Stalin announced that the State Industries Promotion Corporation of Tamil Nadu Ltd (SIPCOT) will set up a mega textile park in the Virudhunagar district.
- Under the Union Budget 2022-23, the total allocation for the textile sector was Rs. 12,382 crore (US$ 1.62 billion). Out of this, Rs.133.83 crore (US$ 17.5 million) is for Textile Cluster Development Scheme, Rs. 100 crore (US$ 13.07 million) for National Technical Textiles Mission, and Rs. 15 crore (US$ 1.96 million) each for PM Mega Integrated Textile Region and Apparel parks scheme and the Production Linked Incentive Scheme.
- For the export of handloom products globally, Handloom Export Promotion Council (HEPC) is participating in various international fairs/events with handloom exporters/weavers to sell their handloom products in the international markets under NHDP.
- The Ministry of Textiles has also been implementing Handloom Marketing Assistance (HMA), a component of the National Handloom Development Programme (NHDP), all across India. HMA provides a marketing platform to the handloom weavers/agencies to sell their products directly to the consumers and develop and promote the marketing channel through organizing expos/events in domestic as well as export markets.
- In November 2021, Union Minister of Textiles, Commerce and Industry, Consumer Affairs & Food and Public Distribution, Mr. Piyush Goyal, stated the desire to target a 3-5x time increase in the export of technical textiles worth US$ 10 billion over the next three years.
- The Indian government has notified uniform goods and services tax rate at 12% on man-made fabrics (MMF), MMF yarns, MMF fabrics and apparel, which came into effect from January 1, 2022.
- Union Minister of Textiles, Commerce and Industry, Consumer Affairs & Food and Public Distribution, Mr. Piyush Goyal announced a mega handloom cluster in Manipur and a handloom and handicraft village at Moirang in Bishnupur. The mega cluster will be set up at an estimated cost of Rs. 30 crore (US$ 4.03 million) under the National Handloom Development Programme (NHDP).
- In October 2021, Union Minister for Commerce and Industry, Textiles, Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution, Mr. Piyush Goyal, announced the creation of 100 textile machinery champions in the country and to promote it in the global market. Through this, the government aims to make India a global player in textiles machinery.
- In October 2021, the Ministry of Textiles approved continuation of the comprehensive handicrafts cluster development scheme with a total outlay of Rs. 160 crore (US$ 21.39 million). Through this scheme, the government aims to support domestic SMEs and local artisans.
- In October 2021, the government introduced SAMARTH training at 75 training centers across the country, to accelerate the scheme's coverage among artisans.
- The government allocated funds worth Rs. 17,822 crore (US$ 2.38 billion) between FY16 and FY22 for the 'Amended Technology Up-gradation Fund Scheme' (A-TUFS), to boost the Indian textile industry and enable ease of doing business.
- Techtextil India, a trade fair focused on technical textiles, nonwovens and composites was held from 25th to 27th November 2021 in Mumbai. Tamil Nadu government signed up for Techtextil India 2021 to strengthen indigenous textile production and attract textile investments into the State. The State government promoted technical textile policies through both physical and virtual segments of the hybrid fair organised by Messe Frankfurt Trade Fairs India.
- In August 2021, Minister of State (MoS), Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas and Labour & Employment, Mr. Rameswar Teli launched ONGC-supported Assam handloom project 'Ujjwal Abahan' through the virtual platform. The project will support and train >100 artisans of Bhatiapar of Sivasagar, Assam in Hathkharga handicraft.
- In August 2021, Flipkart and Himachal Pradesh State Handicrafts and Handloom Corporation Ltd. (HPSHHCL) signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) to help the state's master craftsmen, weavers and artisans showcase their hallmark products on e-commerce platforms.
- In August 2021, Union Minister of Textiles, Commerce and Industry, Consumer Affairs & Food and Public Distribution, Mr. Piyush Goyal said that steps needed to be taken to boost production capacities of handloom sector from the existing Rs. 60,000 crore (US$ 8.06 billion) to 125,000 crore (US$ 16.80 billion) in the next three years. He added that target must be set to increase exports of handloom items from existing Rs. 2,500 crore (US$ 335.92 million) to Rs. 10,000 crore (US$ 1.34 billion). He also announced that a committee would be constituted consisting of all weavers, trainer equipment makers, marketing experts and other stake holders to recommend ways and means to achieve these objectives and enhance overall progress of the handloom sector.
- In July 2021, the government extended the Rebate of State and Central Taxes and Levies (RoSCTL) scheme for exports of apparel/garments and made ups until March 2021. This will help boost exports and enhance competitiveness in the labour-intensive textiles sector.
- To support the handloom weavers/weaver entrepreneurs, the Weaver MUDRA Scheme was launched to provide margin money assistance at 20% of the loan amount subject to a maximum of Rs. 10,000 (US$ 134.22) per weaver. The loan is provided at an interest rate of 6% with credit guarantee of three years.
- Gorakhpur is on track to become a major garment manufacturing centre, boosting the economy in eastern Uttar Pradesh. The Gorakhpur Industrial Development Authority (GIDA) will provide four acres of land for construction of a flattened factory and will enable access to entrepreneurs.
- In March 2021, The Ministry of Textiles favoured limited deal for the India-UK free trade agreement that could boost the garments sector.
- In 2020-21, the UK is India's fourteenth largest trading partner, accounting for US$ 8.7 billion in exports and US$ 6.7 billion in imports.
- Under the proposed trade agreement, the Textile Ministry expects more market access for the Indian textiles and clothing sector in order to achieve its full potential.
- In March 2021, under the ongoing sub-mission on agroforestry (SMAF) scheme, the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with the Central Silk Board, under the Ministry of Textiles, on a convergence model to implement agroforestry in the silk sector.
- Effective 1 January 2021, to boost exports, the government has extended the benefit of the Scheme for Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) to all exported goods
- Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is helping the Indian textile industry to produce yarns and eliminate dependence on import of Chinese and other foreign clothing for military uniforms. Indian defence sector has expressed support towards the Indian technical textile sector.
- In March 2021, while addressing the 9th edition of TECHNOTEX 2021 organized by FICCI, General Bipin Rawat, Chief of Defence Staff appreciated the innovations in Indian technical textiles and stated that the armed forces will rather reduce imports and instead procure technical textiles from Indian industries as a part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
ACHIEVEMENTS
Following are the achievements of the Government in the past four years:
- In June 2021, KVIC recorded a 7.71% growth in gross annual turnover to Rs. 95,741.74 crore (US$ 12.85 billion) from Rs. 88,887 crore (US$ 11.93 billion) in FY20.
- In CY2020, Cotton Corporation of India made a record procurement of ~ 151 lakh bales under MSP operations, which is ~ 290% higher than 38.43 lakh bales procured during the corresponding period last year.
- Under the Scheme for Integrated Textile Parks (SITP), 59 textile parks were sanctioned, out of which, 22 have been completed.
- Employment increased to 45 million in FY19 from 8.03 in FY15.
- Sangam India Ltd, one of the foremost producers in PV dyed yarn, cotton and OE yarn and also ready to stitch fabric, has installed two solar power plants of 5 MW that, on average, helps them to bring down their carbon footprint by at least 20% per annum. SIL also plans to increase the use of recycled fibre, leading to lesser consumption of plastic waste by using it as a raw material.
ROAD AHEAD
India is working on major initiatives, to boost its technical textile industry. Owing to the pandemic, the demand for technical textiles in the form of PPE suits and equipment is on rise. The government is supporting the sector through funding and machinery sponsoring.
Top players in the sector are attaining sustainability in their products by manufacturing textiles that use natural recyclable materials.
The future of the Indian textiles industry looks promising, buoyed by strong domestic consumption as well as export demand. With consumerism and disposable income on the rise, the retail sector has experienced a rapid growth in the past decade with the entry of several international players like Marks & Spencer, Guess and Next into the Indian market.
High economic growth has resulted in higher disposable income. This has led to rise in demand for products creating a huge domestic market.

Note: Conversion rate used in October 2021, Rs. 1 = US$ 0.013
References: Ministry of Textiles, Indian Textile Journal, Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion, Press Information Bureau
Note: ^ - According to 4th Advanced Estimates, CY - Calendar Year
Disclaimer: This information has been collected through secondary research and IBEF is not responsible for any errors in the same.
Major Textiles hubs in India
- NCR
- Gujarat
- Maharashtra
- Uttar Pradesh
- West Bengal
- Tamil Nadu
- Madhya Pradesh
- Rajasthan

Industry Contacts
- The Textile Association (India) (TAI)
- Northern India Textile Mills’ Association (NITMA)
- The Cotton Textiles Export Promotion Council (TEXPROCIL)
- The South India Textile Research Association (SITRA)