INTRODUCTION
The services sector is not only the dominant sector in India's GDP, but has also attracted significant foreign investment, has contributed significantly to export and has provided large-scale employment. India's services sector covers a wide variety of activities such as trade, hotel and restaurants, transport, storage and communication, financing, insurance, real estate, business services, community, social and personal services, and services associated with construction.

MARKET SIZE
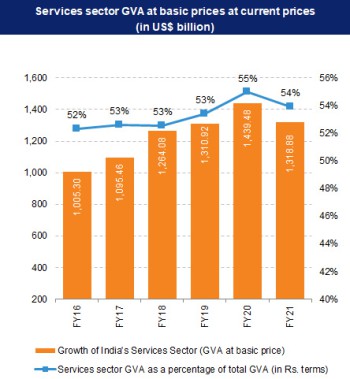
The services sector of India remains the engine of growth for India's economy and contributed 53% to India's Gross Value Added at current prices in FY22 (until January 2022). India's services sector GVA increased at a CAGR of 11.43% to Rs. 101.47 trillion (US$ 1,439.48 billion) in FY20, from Rs. 68.81 trillion (US$ 1,005.30 billion) in FY16. Between FY16 and FY20, financial, real estate and professional services augmented at a CAGR of 11.68% (in Rs. terms), while trade, hotels, transport, communication and services related to broadcasting rose at a CAGR of 10.98% (in Rs. terms).
India's IT and business services market is projected to reach US$ 19.93 billion by 2025.
Services exports comprise a major part of the total export from India. According to the RBI, between April-September 2021, India's service exports stood at US$ 117.6 billion, whereas imports stood at US$ 65.20 billion.
In February 2022, the Purchasing Managers' Index stood at 51.8, compared with 51.5 recorded in January 2022.
The India Services Business Activity Index/ Nikkei/IHS Markit Services Purchasing Managers' Index stood at 55.2 in September 2021, compared with 56.7 in August 2021.
In February 2022, the Purchasing Managers' Index stood at 51.8, compared with 51.5 recorded in January 2022.
INDUSTRY DEVELOPMENTS
Some of the developments in the services sector in the recent past are as follows:
- In October 2021, India's service exports increased by 23.52% to reach US$ 20.86 billion, while imports stood at US$ 12.71 billion.
- In June 2021, India's exports increased by 48.34% to US$ 32.5 billion, marking the seventh consecutive month of growth.
- The Indian services sector was the largest recipient of FDI inflows worth US$ 88.95 billion between April 2000 and June 2021. The services category ranked 1st in FDI inflow as per data released by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
- In the first-half of 2021, private equity investments in India stood at US$ 11.82 billion, as compared with US$ 5.43 billion in the same period last year.
- In August 2021, the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) issued a letter of intent (LoI) to OneWeb (backed by Bharti Group) for satellite communication services licence.
- In July 2021, Tata Teleservices collaborated with Zoom Video Communications to offer bundled communication services.
- In April 2021, the Ministry of Education (MoE) and University Grants Commission (UGC) started a series of online interactions with stakeholders to streamline forms and processes to reduce compliance burden in the higher education sector, as a follow-up to the government's focus on ease of doing business to enable ease of living for stakeholders.
- By October 2021, the Health Ministry's eSanjeevani telemedicine service, crossed 14 million (1.4 crore) teleconsultations since its launch, enabling patient-to-doctor consultations, from the confines of their home, and doctor-to-doctor consultations.
- In April 2021, Elon Musk's SpaceX has started accepting pre-orders for the beta version of its Starlink satellite internet service in India for a fully refundable deposit of US$ 99. Currently, the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) is screening the move and more developments will be unveiled soon.
- In December 2020, a cohort of six health-tech start-ups—AarogyaAI, BrainSightAI, Fluid AI, InMed Prognostics, Wellthy Therapeutics, and Onward Assist—have been selected by the India Edison Accelerator, fueled by GE Healthcare. India Edison Accelerator, the company's first start-up partnership programme focused on Indian mentors, creates strategic partners to co-develop healthcare solutions.
- The Indian healthcare industry is expected to shift digitally enabled remote consultations via teleconsultation. The telemedicine market in India is expected to increase at a CAGR of 31% from 2020 to 2025.
- In December 2020, Gamma Skills Automation Training introduced a unique robotics & automation career launch programme for engineers, an 'Industry 4.0 Hands-on Skill Learning Centre' located at IMT Manesar, Gurgaon in Haryana.
- In December 2020, the 'IGnITE' programme was initiated by Siemens, BMZ and MSDE to encourage high-quality training and technical education. 'IGnITE' aims to develop highly trained technicians, with an emphasis on getting them ready for the industry and future, based on the German Dual Vocational Educational Training (DVET) model. By 2024, this programme aims to upskill ~40,000 employees..
- In October 2020, Bharti Airtel entered cloud communications market with the launch of business-centric 'Airtel IQ'.
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES
The Government of India recognises the importance of promoting growth in services sector and provides several incentives across a wide variety of sectors like health care, tourism, education, engineering, communications, transportation, information technology, banking, finance and management among others.
The Government of India has adopted few initiatives in the recent past, some of these are as follows:
- In October 2021, Prime Minister, Mr. Narendra Modi, approved the establishment of 157 new medical colleges to boost accessibility of affordable health treatments among citizens.
- In October 2021, the government launched a production linked incentive (PLI) scheme to boost manufacturing of telecom and networking products in India. The scheme is expected to attract an investment of ~Rs. 3,345 crore (US$ 446.22 million) over the next four years and generate additional employment for >40,000 individuals.
- In October 2021, the government launched phase-II of the Mahatma Gandhi National Fellowship to empower students and boost skill development.
- In October 2021, the PM Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission was launched by the government, to strengthen the critical healthcare network across India in the next four to five years.
- In September 2021, India and the UK joined the 11th Economic and Financial Dialogue (EFD) to discuss the FTA (Free Trade Agreement) opportunities in services.
- Credit to non-food industries stood at Rs. 110.86 trillion (US$ 1.49 trillion), as of November 5, 2021.
- The Indian government is planning to introduce a credit incentive programme worth Rs. 50,000 crore (US$ 6.8 billion) to boost healthcare infrastructure in the country. The programme will allow companies to access funds to ramp up hospital capacity or medical supplies with the government acting as a guarantor.
- In June 2021, India and Australia announced its collaboration in cyber-enabled critical technologies, highlighting the requirement to boost the critical information security infrastructure such as 5G telecom networks.
- Under Union Budget 2021-22, the government allocated Rs. 7,000 crore (US$ 963.97 million) to the BharatNet programme to boost digital connectivity across India.
- FDI limit for insurance companies has been raised from 49% to 74% and 100% for insurance intermediates.
- In May 2021, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry announced that India received an FDI inflow of US$ 81.72 billion, the highest FDI during FY 2020-21.
- In March 2021, the central government infused Rs. 14,500 crore (US$ 1.99 billion) capital in Central Bank of India, Indian Overseas Bank, Bank of India and UCO Bank through non-interest bearing bonds.
- On January 15, 2021, the third phase of Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) was launched in 600 districts with 300+ skill courses. Spearheaded by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, the third phase will focus on new-age and COVID-related skills. PMKVY 3.0 aims to train eight lakh candidates.
- In January 2021, the Department of Telecom, Government of India, signed an MoU with the Ministry of Communications, Government of Japan, to strengthen cooperation in the areas of 5G technologies, telecom security and submarine optical fibre cable system.
- On November 4, 2020, the Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister, Mr. Narendra Modi, approved to sign a memorandum of understanding (MoU) between the Ministry of Communication and Information Technology and the Department of Digital, Culture, Media and Sports (DCMS) of United Kingdom Government to cooperate in the field of telecommunications/information and communication technologies (ICTs).
- In October 2020, the government selected Hughes Communications India to connect 5,000 village panchayats in border and naxal-affected states and island territories with satellite broadband under BharatNet project by March 2021.
- In September 2020, the government announced that it may infuse Rs. 200 billion (US$ 2.72 billion) in public sector banks through recapitalisation of bonds
- In the next five years, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology is working to increase the contribution of the digital economy to 20% of GDP. The government is working to build cloud-based infrastructure for collaborative networks that can be used for the creation of innovative solutions by AI entrepreneurs and startups.
- On Independence Day 2020, Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi announced the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM) to provide a unique health ID to every Indian and revolutionise the healthcare industry by making it easily accessible to everyone in the country. The policy draft is under 'public consultation' until September 21, 2020.
- In September 2020, the Government of Tamil Nadu announced a new electronics & hardware manufacturing policy aligned with the old policy to increase the state's electronics output to US$ 100 billion by 2025. Under the policy, it aims to meet the requirement for incremental human resource by upskilling and training >100,000 people by 2024.
- Government of India has launched the National Broadband Mission with an aim to provide Broadband access to all villages by 2022.
ROAD AHEAD
By 2025, healthcare industry is expected to reach US$ 372 billion. India's digital economy is estimated to reach US$ 1 trillion by 2025. By end of 2023, India's IT and business services sector is expected to reach US$ 14.3 billion with 8% growth.
The implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) has created a common national market and reduced the overall tax burden on goods. It is expected to reduce costs in the long run-on account of availability of GST input credit, which will result in the reduction in prices of services.
India's software service industry is expected to reach US$ 1 trillion by 2030.
Note: Conversion rate used for October 2021 is Rs. 1 = US$ 0.013
References: Media Reports, Press Releases, DPIIT publication, Press Information Bureau
Note: *- Services sector includes Financial, Banking, Insurance, Non-Financial / Business, Outsourcing, R&D, Courier, Tech Testing and Analysis, Other
Disclaimer: This information has been collected through secondary research and IBEF is not responsible for any errors in the same.

Major Service sector states
- Karnataka
- Kerela
- Jammu and Kashmir
- Bihar
- Sikkim
- West Bengal
- Mizoram
- Manipur

Industry Contacts
- Indian Banks' Association
- Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA)
- Hotel Association of India (HAI)
- National Association of Software and Services Companies (NASSCOM)
- Services Export Promotion Council (SEPC)