INTRODUCTION
Infrastructure sector is a key driver for the Indian economy. The sector is highly responsible for propelling India’s overall development and enjoys intense focus from Government for initiating policies that would ensure time-bound creation of world class infrastructure in the country. Infrastructure sector includes power, bridges, dams, roads, and urban infrastructure development.

MARKET SIZE
According to the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), FDI in construction development (townships, housing, built-up infrastructure and construction development projects) and construction (infrastructure) activity sectors stood at US$ 26.17 billion and US$ 26.30 billion, respectively, between April 2000-December 2021. In FY21, infrastructure activities accounted for 13% share of the total FDI inflows of US$ 81.72 billion.
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES
- In March, Mr. Nitin Gadkari, Minister for Road Transport and Highways inaugurates 19 National Highway projects in Haryana and Rajasthan totalling Rs 1,407 crore (US$ 183.9 million).
- The government expanded the ‘National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP)’ to 9,335 projects. ~217 projects worth Rs. 1.10 lakh crore (US$ 15.09 billion) were completed as of 2020.
- In November 2021, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) has approved a US$ 250-million loan to support development of the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme (NICDP). This is a part of the US$ 500-million loan to build 11 industrial corridors bridging 17 states.
- In November 2021, India, the US, Israel and the UAE established a new quadrilateral economic forum to focus on infrastructure development projects in the region and strengthen bilateral co-operation.
- The initiative ‘Infrastructure for Resilient Island States’ (launched in November 2021) will give India a huge opportunity to contribute to the betterment of other vulnerable countries in the world.
- In October 2021, the Union Cabinet of India approved the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan—including implementation, monitoring and support mechanism—for providing multi-modal connectivity.
- As a part of the GatiShakti National Master Plan, the government is planning to launch geospatial digital platform to facilitate planning and monitoring of projects ranging from telecom networks, gas pipelines to road and railways.
- In October 2021, the Dubai government and India, inked an agreement to develop infrastructure such as industrial parks, IT towers, multipurpose towers, logistics centres, a medical college and a specialised hospital in Jammu & Kashmir.
- In FY22, government initiatives such the National Infrastructure Pipeline, National Monetisation Pipeline, Bharatmala Pariyojana, changes in the Hybrid Annuity Model (HAM) and fast pace of asset monetization to boost road construction.
- As of October 2021, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways constructed national highways extending 4,450 kms compared with 4,956 kms, as of October 2020.
- In September 2021, National Mineral Development Corporation Ltd. (NMDC) R&D Centre collaborated with CSIR-IMMT (Institute of Minerals and Materials Technology) to pursue combined research projects on iron ore mining technologies.
- In September 2021, the Indian government announced road projects worth Rs. 1 lakh crore (US$ 13.48 billion) to develop road infrastructure in Jammu and Kashmir. The region also recorded growth in national highways, from 7 in 2014 to 11 in 2021.
- On September 29, 2021, NTPC Renewable Energy ltd (REL), a 100% subsidiary of NTPC ltd, signed its first green term loan agreement with Bank of India for Rs. 500 crore (US$ 67.28 million) at a competitive rate and a tenor of 15 years for its 470 MW solar projects in Rajasthan and 200 MW solar projects in Gujarat.
- In August 2021, the Government of India, the Central Water Commission (CWC), government representatives from 10 participating states and the World Bank signed a US$ 250 million project to support the Indian government’s long-term dam safety programme and improve safety and performance of existing dams across various states.
- oThe Second Dam Rehabilitation and Improvement Project (DRIP-2) will strengthen dam safety by building dam safety guidelines, bring in global experience and introduce innovative technologies. The project will be implemented in ~120 dams across Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Manipur, Meghalaya, Odisha, Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu, and at the national level through the CWC.
- In August 2021, Union Minister of Road Transport Highways, Mr. Nitin Gadkari announced to launch 1,080-km (road construction) projects worth Rs. 25,370 crore (US$ 3.4 billion) in Gujarat under the Bharatmala Pariyojana—the ambitious road and highways project that aims to build highways from Maharashtra, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana and then cover the entire string of Himalayan territories.
- In July 2021, the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways allocated Rs. 165 crore (US$ 22 million) under Economic Importance and Inter State Connectivity Scheme (EIC&ISC) for FY22.
- In July 2021, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways granted 162-km road highway (New NH-365BG), as part of the economic corridor under the Bharatmala Pariyojana, with an aim to connect Andhra Pradesh and Telangana via a robust road infrastructure that supports speed of 100kms/hour. The total project cost is Rs. 2,600 crore (US$ 350 million).
- In July 2021, Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners (CIP) signed an investment agreement with Amp Energy India Pvt Ltd. to enable joint equity investments of >US$ 200 million in renewable energy projects in India, with the potential for future expansion.
- To encourage rooftop solar (RTS) throughout the country, notably in rural regions, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy is undertaking Rooftop Solar Programme Phase II, which aims to install RTS capacity of 4,000 MW in the residential sector by 2022 with a provision of subsidy.
- The Ministry of Commerce's Logistics Division presented its plans for ‘Freight Smart Cities’ in July 2021, with goal of improving the efficiency of urban freight and lowering logistics expenses. Over the next 10 years, demand for urban freight is predicted to increase by 140%. Final-mile freight transit in Indian cities accounts for 50% of the total logistics expenditures in the country's increasing e-commerce supply chains. According to ICRA ratings, the domestic road logistics sector is predicted to grow by 6-9% in FY22.
- The XV Finance Commission recommended Rs. 8,000 crore (US$ 1,077 million) performance-based challenge money to states for new city incubation in July 2021. Each proposed new city has a budget of Rs. 1,000 crore (US$ 134 million) and each state can only have one new city under the proposed concept.
- In July 2021, NTPC announced to invest Rs. 2-2.5 crore (US$ 0.27-0.34 million) over the next 10 years to expand renewable capacity and invited bids for an engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) package, with land development for 500 MW of grid-connected solar projects anywhere in India.
- In July 2021, the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, the government-owned GAIL lined up Rs. 5,000 crore (US$ 671.14 million) for setting up two plants each for producing ethanol and compressed biogas (CBG) from municipal waste.
- In June 2021, Mr. Rajnath Singh, the Minister of Defence e-inaugurated 20 kms long double lane Kimin-Potin road, together with nine other roads in Arunachal Pradesh and one each in the Union Territories of Ladakh and Jammu & Kashmir, built by Border Roads Organisation (BRO).
- In June 2021, Mr. Prakash Javadekar, the ex-Minister of Heavy Industries and Public Enterprises, inaugurated NATRAX, the 1000-acre high-speed track (HST) in Indore. This is Asia's longest track and can be used for a variety of high-speed performance testing on a wide range of vehicles.
- In June 2021, the NTPC floated a global Expression of Interest (EOI) to set up two pilot projects for standalone fuel cell-based backup power system and a standalone fuel cell-based microgrid system with hydrogen production using electrolyser at NTPC premises. Through the projects, NTPC is looking to further strengthen its footprint in green and clean fuel. The NTPC will collaborate for implementation and further commercialisation of the projects.
- In May 2021, Minister for Road Transport & Highways and Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises, Mr. Nitin Gadkari stated that the government is giving utmost priority to infrastructure development and has set a target of road construction of worth Rs.15 lakh crore (US$ 206 billion) in the next two years.
- The Ministry of Railways plans to monetise assets including Eastern and Western Dedicated Freight Corridors after commissioning, induction of 150 modern rakes through PPP, station redevelopment through PPP, railway land parcels, multifunctional complexes (MFC), railway colonies, hill railways and stadiums.
- In March 2021, the government announced a long-term US$ 82 billion plan to invest in the country’s seaports. ~574 projects have been identified, under the Sagarmala project, for implementation through 2035.
- In April 2021, the Ministry of Power (MoP) released the draft National Electricity Policy (NEP) 2021. The MoP created an expert committee including members from state governments, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), NITI Aayog and the Central Electricity Authority (CEA).
- In March 2021, the Parliament passed a bill to set up the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) to fund infrastructure projects in India.
- Indian railways received Rs. 1,10,055 crore (US$ 15.09 billion), of which Rs. 1,07,100 crore (US$ 14.69 billion) is for capital expenditure.
- Rs. 1,18,101 crore (US$ 16.20 billion) has been allocated towards road transport and highway sector.
- In Budget 2021, the government announced the following interventions under Pradhan Mantri Aatmanirbhar Swasth Bharat Yojana (PMANSY):
- An outlay of Rs. 64,180 crore (US$ 8.80 billion) over six years to strengthen the existing ‘National Health Mission’ by developing capacities of primary, secondary & tertiary care and healthcare systems & institutions to detect and cure new and emerging diseases.
- This scheme will strengthen 17,000 rural and 11,000 urban health and wellness centres.
- Setting up integrated public health labs in all districts and 3,382 block public health units in 11 states.
- Establishing critical care hospital blocks in 602 districts and 12 central institutions.
- Strengthening the NCDC (National Centre for Disease Control) to have five regional branches and 20 metropolitan health surveillance units.
- Expanding integrated health information portal to all states/UTs.
- Rolling out the pneumococcal vaccine, a ‘Made in India’ product, across the country.
- Rs. 35,000 crore (US$ 4.80 billion) has been allocated for COVID-19 vaccines in FY22.
- The government announced Rs. 18,998 crore (US$ 2.61 billion) for metro projects.
- Mega Investment Textiles Parks (MITRA) scheme was launched to establish world-class infrastructure in the textile sector and establish seven textile parks over three years.
- The government announced Rs. 305,984 crore (US$ 42 billion) over the next five years for a revamped, reforms-based and result-linked new power distribution sector scheme.
ROAD AHEAD
The infrastructure sector has become the biggest focus area for the Government of India. India plans to spend US$ 1.4 trillion on infrastructure during 2019-23 to have a sustainable development of the country. The Government has suggested investment of Rs. 5,000,000 crore (US$ 750 billion) for railways infrastructure from 2018-30.
India and Japan have joined hands for infrastructure development in India's Northeast states and are also setting up an India-Japan Coordination Forum for Development of Northeast to undertake strategic infrastructure projects for the region.
Note: Conversion rate used for November 2021 is Rs. 1 = US$ 0.013
References:Media Reports, Press releases, National Infrastructure Pipeline, Union Budget 2021-22, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Economic Survey-2020-21
Disclaimer: This information has been collected through secondary research and IBEF is not responsible for any errors in the same.

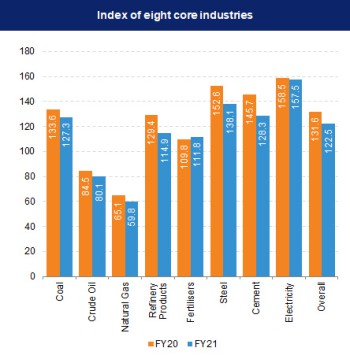
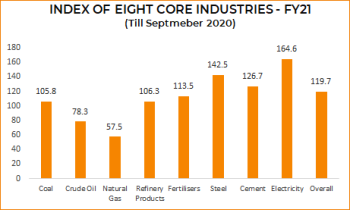
Infrastructure Clusters
- Coal
- Crude Oil
- Natural Gas
- Refinery Products
- Fertilizers
- Steel
- Cement
- Electricity
- Overall
Industry Contacts
- Public Private Partnerships in India
- Building Materials & Technology Promotion Council