INTRODUCTION
The Micro Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) sector is a major contributor to the socio-economic development of the country. In India, the sector has gained significant importance due to its contribution to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of the country and exports. The sector has also contributed immensely with respect to entrepreneurship development especially in semi-urban and rural areas of India.
According to the provisions of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006 the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) are classified in two classes i.e., Manufacturing Enterprises and Service Enterprises.
The enterprises are further categorized based on investment in equipment and annual turnover.

| Criteria | Manufacturing | Service | ||
| Turnover | Investment | Turnover | Investment | |
| Micro | Rs. 5 crore(US$ 0.6 million) | Less than Rs. 25 lakh (US$ 0.03 million) | Rs. 5 crore(US$ 0.6 million) | Less thanRs. 10 lakh(US$ 0.01 million) |
| Small | Rs. 50 crore(US$ 6.8 million) | More than Rs. 25 lakh (US$ 0.03 million) but less than Rs. 5 crore (US$ 0.6 million) | Rs. 50 crore(US$ 6.8 million) | More than Rs. 10 lakh (US$ 0.01 million) but less than Rs. 2 crore (US$ 0.3 million) |
| Medium | Rs. 250 crore (US$ 34 million) | More than Rs. 5 crore (US$ 0.6 million), but less than Rs. 10 crore (US$ 1.4 million) | Rs. 250 crore (US$ 34 million) | More than Rs. 2 crore(US$ 0.3 million) but does not exceed Rs. 5 crore(US$ 0.6 million) |
MARKET SIZE

The BSE SME (small and medium enterprises) platform is expected to witness >60 SMEs to enter the market in one year (2021-22) to bring up equity funds for meeting their business requirements. The initial public offering (IPO) route witnessed 16 SMEs enter the market; they raised Rs. 100 crore (US$ 13.74 million) in 2020. In June 2021, Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) announced that it has collaborated with Electronics and Computer Software Export Promotion Council (ESC) to build awareness among small businesses and start-ups about advantages of listing.
MSMEs are being encouraged to market their products on the e-commerce site, especially through Government e-Marketplace (GeM), owned and run by the government, wherefrom Ministries and PSUs (public sector undertakings) source their procurement. As of March 24, 2022, the GeM portal has served 9.63 million orders worth Rs. 219,071 crore (US$ 28.70 billion) from 4 million registered sellers and service providers for 59,259 buyer organisations.
Domestic business requires a strong financial stimulus with concessional working capital loans to ensure adequate liquidity is maintained in business operations from the government and financial institutes.
Indian Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) are rapidly adopting digital payments over cash, with 72% payments done through the digital mode compared with 28% cash transactions. Rise in digital adoption presents prospects for further growth in the sector.
STATUTORY BODIES
MSME Ministry has four statutory bodies namely, Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) who is responsible for promoting and developing khadi and village industries for providing employment opportunities in rural areas, thereby strengthening the rural economy, Coir Board in charge of promoting overall development of the coir industry and improving living conditions of workers in this industry, National Small Industries Corporation Limited (NSIC) responsible for promoting, aiding and fostering growth of micro and small enterprises in the country, generally on commercial basis, National Institute for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises, (NI-MSME) in-charge of enterprise promotion and entrepreneurship development, enabling enterprise creation, performing diagnostic development studies for policy formulation, etc. and lastly, Mahatma Gandhi Institute for Rural Industrialisation (MGIRI) responsible for accelerating rural industrialisation for sustainable village economy, attract professionals and experts to Gram Swaraj, empower traditional artisans, encourage innovation through pilot study/field trials and R&D for alternative technology using local resources. New online system of MSME/Udyam Registration launched by the Union MSME Ministry, w.e.f. July 01, 2020, successfully registered >1.1 million MSMEs until November 2020. In June 2021, the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises extended the validity of Udyog Aadhaar Memorandum from March 31, 2021, to December 31, 2021.
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
- In November 2021, the Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) inked a pact with Google to pilot social impact lending with financial assistance up to Rs. 1 crore (US$ 133,939.60) at subsidised interest rates to micro enterprises. To reinvigorate the Indian MSME sector, Google India Pvt. Ltd. GIPL, will bring a corpus of US$ 15 million (~Rs. 110 crore) for micro enterprises as a crisis response related to COVID-19.
- In November 2021, digital freight forwarder Freightwalla, launched a shipment tracking service for MSME exporters and importers based on predictive analytics to help businesses tackle risks associated with shipment delays and improve supply chain efficiency.
- In November 2021, Cashinvoice, a supply chain financing (SCF) platform, announced that it will aid MSMEs with over Rs. 10,000 crore (US$ 1.33 billion) worth of financing in the year ahead, as it has raised Pre-Series A funding of US$ 1 million from Accion Venture Lab.
- In October 2021, Sundaram Finance and the MSME Development Institute (Chennai), provided marketing assistance to MSMEs. Entrepreneurial and managerial development of MSMEs will be done through an incubator scheme, that will give innovators opportunities to develop and nurture ideas for the production of new products.
- In September 2021, Aerospace Engineers Private Limited, a Tamil Nadu-based MSME, secured a contract from Boeing to produce and supply critical aviation components.
- In September 2021, Walmart and Flipkart announced the completion of the first phase of training of >2,500 MSMEs under Vriddhi, the supplier development programme.
- In September 2021, Flipkart introduced 'Flipkart Boost’ to help digital-first consumer brands and empower MSMEs.
- In September 2021, HDFC Bank collaborated with the National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC) to offer credit support to the micro, small and medium enterprise (MSME) sector.
- In August 2021, the US Agency for International Development (USAID) and the US International Development Finance Corporation (DFC) collaborated with Kotak Mahindra Bank to support MSMEs.
- In August 2021, Facebook India, in collaboration with Indifi, announced ‘Small Business Loans Initiative’, a new programme to support small and medium businesses (SMBs) get quick access to credit via independent lending partners.
- In August 2021, Indian Bank introduced 'MSME Prerana', an online business-mentoring programme for MSMEs in Odisha. In FY21, the state (Odisha) accounted for ~5% of the total MSME credit exposure of Indian Bank and recorded an increase of 39% YoY.
- In July 2021, Amazon India announced to expand its existing nine fulfilment centres and launch additional 11 new centres. This expansion plan is expected to create direct and indirect job opportunities in India and further strengthen Amazon’s foothold in the country.
- In July 2021, Razorpay acquired TERA Finlabs, a provider of embedded financing solutions, to strengthen capabilities in data-driven risk management, capital solutions and credit underwriting to financially support MSMEs.
- In July 2021, Amazon India introduced Digital Kendra in Surat—its first brick and mortar resource centre to assist ‘kiranas’ and small businesses to go digital.
- In July 2021, the Federation of Indian Export Organisations (FIEO) signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with Aramex India, logistics services provider, to support MSME exporters in India.
- In June 2021, Tide, a UK-based business financial platform, announced to invest >Rs. 1,000 crore (US$ 134.21 million) in India over the next five years to tap the rising SME (small and medium-sized enterprises) market.
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES
The Government of India has designed various policies for the growth of MSMEs in the country.
- As of March 2022, the number of loans sanctioned under the Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY) scheme was 48.92 million and the amount disbursed was Rs. 3,02,948.49 crore (US$ 39.90 billion).
- In the Union Budget of 2022-23 MSMEs sector was allocated an Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS) of Rs. 50,000 crore (US$ 6.55 billion).
- On March 30 2022, the Indian government allocated Rs. 6,062.45 crore (US$ 808 million) for the scheme Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP). The programme aims to improve market and credit access, strengthen institutions and governance at the centre and state levels, improve centre-state connections and partnerships, resolve late payment difficulties, and green MSMEs.
- In November 2021, the Indian government launched the Special Credit Linked Capital Subsidy Scheme (SCLCSS) for the services sector. This scheme will help enterprises in the services sector meet various technology requirements.
- In November 2021, the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises launched SAMBHAV, a national-level awareness programme to push economic growth by promoting entrepreneurship and domestic manufacturing.
- In September 2021, Union Minister for MSMEs, Mr. Narayan Rane introduced ‘India Export Initiative’ and ‘IndiaXports 2021 Portal’. This initiative will help exports reach its Rs. 2,928,000 crore (US$ 400 billion) target by the end of FY22 and further push it to Rs. 7,320,000 crore (US$ 1 trillion) by FY27.
- In September 2021, Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) established the first ‘Silk Yarn Production Centre’ in Odisha to boost the local silk industry and generate employment.
- In September 2021, Union Minister for MSMEs, Mr. Narayan Rane inaugurated Rohtak Technology Centre, which is expected to train >8,400 trainees annually.
- In September 2021, Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) launched SPIN (Strengthening the Potential of India) scheme and built a pottery cluster under SFURTI Scheme in Varanasi to support >1,100 individuals of the marginalised potters’ community.
- In July 2021, Lok Sabha passed a bill on ‘Factoring Regulation (Amendment)’ to expedite the payments ecosystem for MSMEs.
- Budget allocation for MSMEs in FY22 more than doubled to Rs. 15,700 crore (US$ 2.14 billion) vis-à-vis Rs. 7,572 crore (US$ 1.03 billion) in FY21.
- The government also announced Rs. 3 lakh crore (US$ 40.85 billion) collateral-free automatic loans for businesses.
- In Union Budget 2021, the government announced funds worth Rs. 10,000 crore (US$ 1.36 billion) for ‘Guarantee Emergency Credit Line’ (GECL) facility to eligible MSME borrowers, giving a major boost to the sector.
ACHIEVEMENTS IN THE SECTOR
The Ministry of MSME runs numerous schemes targeted at providing credit and financial assistances, skill development training, infrastructure development, marketing assistance, technological and quality upgradation and other services for MSMEs across the country.
ROAD AHEAD
The Government of India has envisioned doubling the Indian economy to US$ 5 trillion in five years. In order to achieve this goal, career opportunities for the young population have been generated and MSMEs have the potential to serve as a key employment generator. Therefore, the government has taken up promotion of MSMEs in order to create new jobs in the sector. Further, the government aims to enhance MSME’s share in exports and its contribution to GDP.
In order to achieve these targets, the government should invest in providing more back-end services to improve performance of the MSME sector as it supplies goods and services to big industrial enterprises. Lack of technology-based production activities and low investment in R&D activities are bottlenecks hindering the sector to become competent. Globally available technology could be subsidised by the government so that the product quality of MSME players can be improved using the existing resources. This also requires the help of academic institutions in the form of providing research and development (R&D) services for product innovation.
References: Government Websites, Press Releases, Media Reports, Deloitte Report
Note: Conversion rate used in November 2021, Rs. 1 = US$ 0.01336

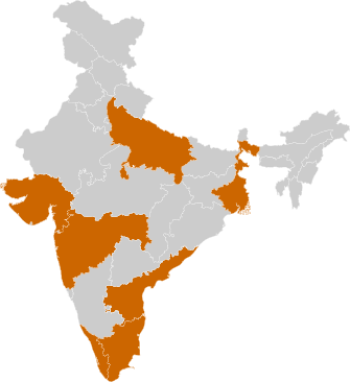
MSME Clusters
- Maharashtra
- Andhra Pradesh
- Gujarat
- Tamil Nadu
- West Bengal
- Uttar Pradesh
- Kerala
Industry Contacts
- National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC)
- Office of Development Commissioner (MSME)
- Khadi Village Industries Commission (KVIC)
- Coir Board
- National Institute for micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (NIMSME)